Imagine a world where sophisticated laboratory tests aren’t confined to a bustling central facility miles away, but can be initiated, managed, and even partially executed from virtually anywhere. For decades, diagnostics have been a cornerstone of healthcare, guiding treatment decisions and monitoring patient health. While central labs have become incredibly efficient, accessing them has often presented logistical hurdles, especially for those in remote areas or critical situations requiring rapid results.
But the landscape is changing, driven by exciting technological advancements. We’re entering an era where the physical distance between the patient and the diagnostic capability is shrinking, thanks to the rise of remote-controlled laboratory diagnostics. This isn’t science fiction; it’s becoming a reality, promising a future where access to timely and accurate testing is significantly improved.
Technological Innovations Powering Remote Diagnostics
Several key technological innovations are converging to make remote-controlled labs viable:
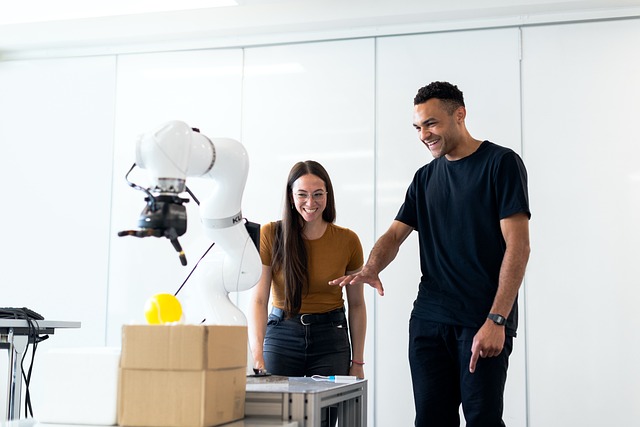
- Advanced Robotics and Automation: Precise robotic arms and automated sample handling systems can perform complex tasks within the lab, from sample preparation to test execution, all controlled remotely by trained personnel.
- High-Speed Connectivity (5G, Satellite): Reliable, low-latency communication networks are essential for transmitting real-time control commands and receiving massive amounts of data (images, raw results) from distant lab equipment.
- Miniaturization and Microfluidics: Lab-on-a-chip technologies and portable diagnostic devices are becoming more sophisticated, allowing complex assays to be performed on smaller sample volumes outside traditional lab settings, potentially with remote oversight or control.
- Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI algorithms can assist in interpreting complex results (like imaging or genetic data), flag anomalies, or even optimize workflows, enabling remote experts to manage multiple tests or locations more effectively.
- Secure Cloud Infrastructure and IoT: Connecting lab instruments and data streams securely to the cloud allows for central monitoring, control, and data management from a distance, forming the backbone of a remote network.
These technologies are enabling a shift from purely manual or locally automated processes to systems where skilled professionals can leverage their expertise across distances, overseeing and directing diagnostic procedures without being physically present at the point of testing.
Health Innovations and the Impact on Patient Care
The integration of remote control into laboratory diagnostics represents a significant health innovation with profound implications:
- Increased Accessibility: Bringing advanced diagnostic capabilities to remote villages, disaster zones, or even a patient’s home (for certain tests) becomes more feasible. This is a game-changer for global health equity.
- Faster Turnaround Times: Eliminating the need to transport samples long distances can drastically reduce the time it takes to get results, critical for diagnosing acute conditions or managing outbreaks.
- Improved Efficiency: Centralizing expert oversight allows a smaller number of highly skilled professionals to manage distributed testing sites, optimizing resource allocation.
- Enhanced Safety: In hazardous environments or during pandemics, remote control minimizes human exposure to infectious agents or dangerous substances.
- Support for Decentralized Healthcare: As healthcare models shift towards community-based or home care, remote diagnostics provide the necessary testing support outside the traditional hospital or clinic setting.
This evolution promises a more responsive, accessible, and efficient diagnostic ecosystem. Healthcare providers can make faster, more informed decisions, and patients, regardless of their location, can benefit from timely and accurate testing that was previously out of reach. The feeling is one of empowerment – leveraging technology to break down barriers and bring essential healthcare services closer to where they are needed most.